
Progress 0%
Ridding the world of unnecessary packaging: Nohbo with Benjamin Stern
World's first land-based coral farm: Coral Vita with Sam Teicher
Climate-resilient agriculture: The Cacao Project with Louise Mabulo
Cleaning up floating ocean plastics: The Ocean CleanUp with Boyan Slat
Eliminating the idea of waste: TerraCycle with Tom Szaky
A circular model for second-hand clothing: FabricAID with Omar Itani
Planting trees, one goal at a time: Trees4Goals with Lesein Mutunkei
Exchanging waste for plants: Eco Star with Fatemah Alzelzela
Innovative technology to reduce rice waste: Rice Inc with Kisum Chan
Key Concepts
Transition
Energy
Efficiency
Carbon Sink
Climate
Neutrality
Carbon Emissions
Reduction
Carbon
Offsetting
Carbon
Neutrality
Environmental
Justice
Circular
Economy
No-Take-Zone
Climate Laws
Climate Justice
Transition
Energy
Efficiency
Carbon Sink
Climate
Neutrality
Carbon Emissions
Reduction
Carbon
Offsetting
Carbon
Neutrality
Environmental
Justice
Circular
Economy
No-Take-Zone
Climate Laws
Climate Justice
Transition
Energy
Efficiency
Carbon Sink
Climate
Neutrality
Carbon Emissions
Reduction
Carbon
Offsetting
Carbon
Neutrality
Environmental
Justice
Circular
Economy
No-Take-Zone
Climate Laws
Climate Justice
Climate Justice
This is a term which acknowledges that climate change can have differing social, economic, public health and other adverse impacts on historically marginalized or vulnerable communities. (Yale Climate Connections) As not all climate impacts are felt equally by all individuals (because of inequalities that are based on socio-demographic characteristics such as differences in gender, ethnicity, age, or income), climate justice strives to have these inequalities addressed through long-term mitigation and adaptation strategies. Climate justice begins by recognizing the key groups and people that are affected differently by climate change and protecting those who are less resilient.
Transition
In the context of environmental sustainability, transition refers to the changes societies need to make in their core systems in order to achieve their long-term sustainability goals. Some of these systems include food production, energy use, transportation, and construction. (1)
Energy
Efficiency
This means using less energy to perform the same task – that is, eliminating energy waste. Energy efficiency brings a variety of benefits: it reduces greenhouse gas emissions, it decreases the demand for energy imports, and it lowers costs on a household and economy-wide level. (Environmental and Energy Study Institute)
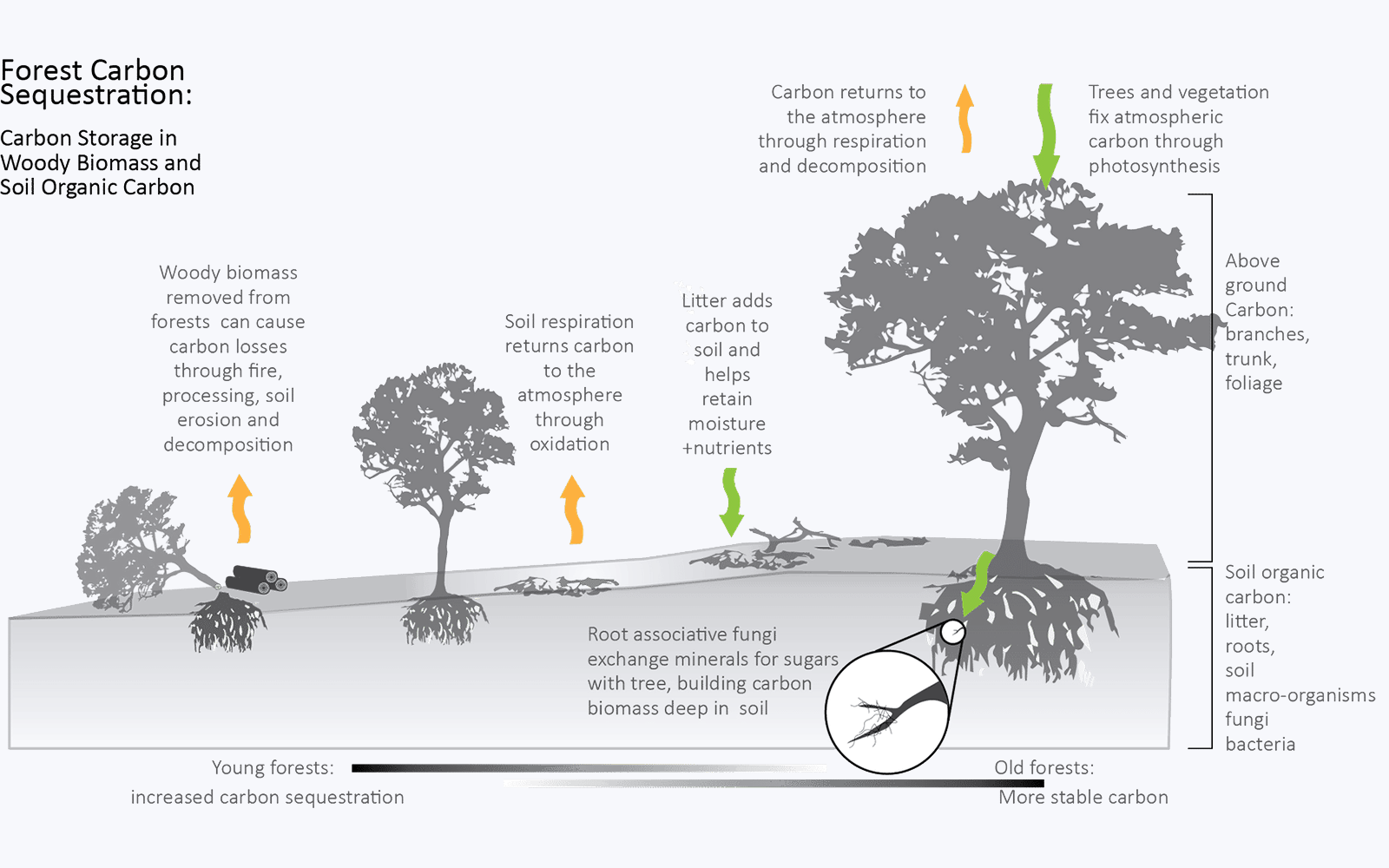
Carbon Sink
This is an area or ecosystem which absorbs more carbon dioxide from the Earth’s atmosphere than it releases. (2) The main natural carbon sinks include soil, oceans and forests. These carbon sinks trap and store atmospheric carbon dioxide in a process called carbon sequestration. However, the carbon stored in natural sinks such as forests can be released back into the atmosphere through forest fires, changes in land use or logging. (3)
Artificial carbon sequestration processes have been developed to extract and store Carbon from the atmosphere or delay/prevent it from being released into the atmosphere. However, artificial carbon sequestration has not acquired the efficiency needed to cope with the extreme effects of climate change. (4) It is crucial to reduce carbon emissions in the first place, in order to aim for climate neutrality. (3)
You can read more about carbon sinks here.
Photo source: Board of Water and Soil Agency
Climate
Neutrality
This refers to reaching and maintaining a balance between emitting greenhouse gases into - and absorbing greenhouse gases from - the atmosphere. It is the same concept as carbon neutrality but it extends to zero net anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions (including emissions beyond carbon dioxide).
Carbon Emissions
Reduction
Reducing carbon emissions refers to the lowering of CO2 gases released into the atmosphere due to human activity. Reducing our carbon emissions helps to ease the pressure on our natural resources and helps slow down climate change. There are various ways of reducing carbon emissions which can have effective impacts on the natural environment. Switching to alternative sources of energy is one of the primary ways to reduce carbon emissions.
Renewable sources of energy such as solar, wind and biomass cannot be depleted and are able to supply a continuous source of clean energy. Even though they still generate some carbon dioxide emissions, these are much lower than the emissions produced by non-renewable resources such as oil or natural gas. Adapting to more sustainable lifestyles and cutting down consumption to preserve nature, forests and biodiversity are still the most impactful ways to prevent irreversible damage.
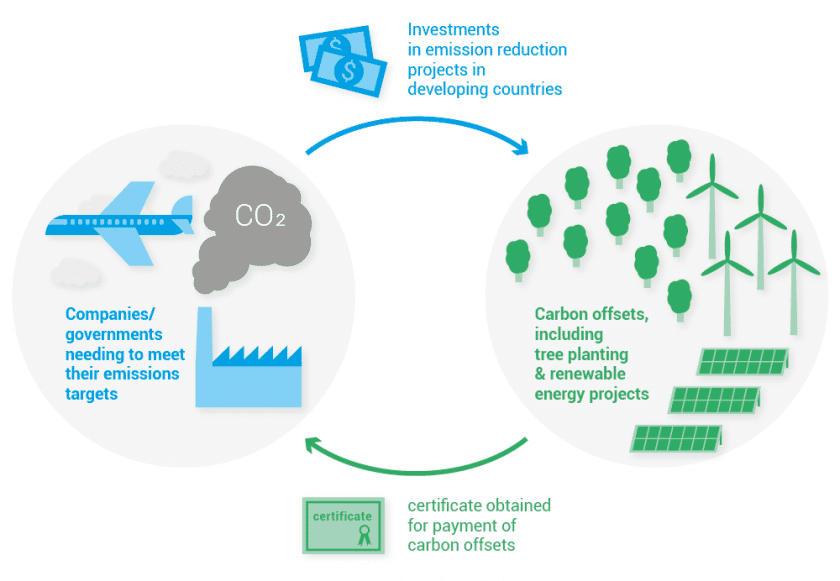
Carbon
Offsetting
This refers to a reduction in GHG emissions – or an increase in Carbon storage (e.g., through land restoration or the planting of trees) – to compensate for emissions that occur elsewhere. Carbon offsetting is possible because climate change is not just a local problem. Greenhouse gases mix throughout the atmosphere, so reducing them anywhere contributes to overall climate protection. (Carbon Offset Guide) Currently, there are many carbon offsetting projects to which individuals and businesses can contribute which help counteract the emission of GHGs. However, individuals need to carefully select carbon offsetting projects which use certified methods to reduce GHG emissions.
Photo source: UNEP
Carbon
Neutrality
This refers to reaching and maintaining a balance between emitting carbon dioxide into - and absorbing carbon dioxide from - the atmosphere. (3) Carbon neutrality means annual zero net anthropogenic (human-caused or influenced) CO2 emissions. By definition, carbon neutrality means every tonne of anthropogenic CO2 emitted into the atmosphere is compensated with an equivalent amount of CO2 removed. (WRI)
Environmental
Justice
This means the fair treatment and meaningful involvement of all people regardless of race, color, national origin, or income with respect to the development, implementation and enforcement of environmental laws, regulations and policies. Fair treatment means no group of people should bear a disproportionate share of the negative environmental consequences resulting from industrial, governmental and commercial operations or policies. (EPA)
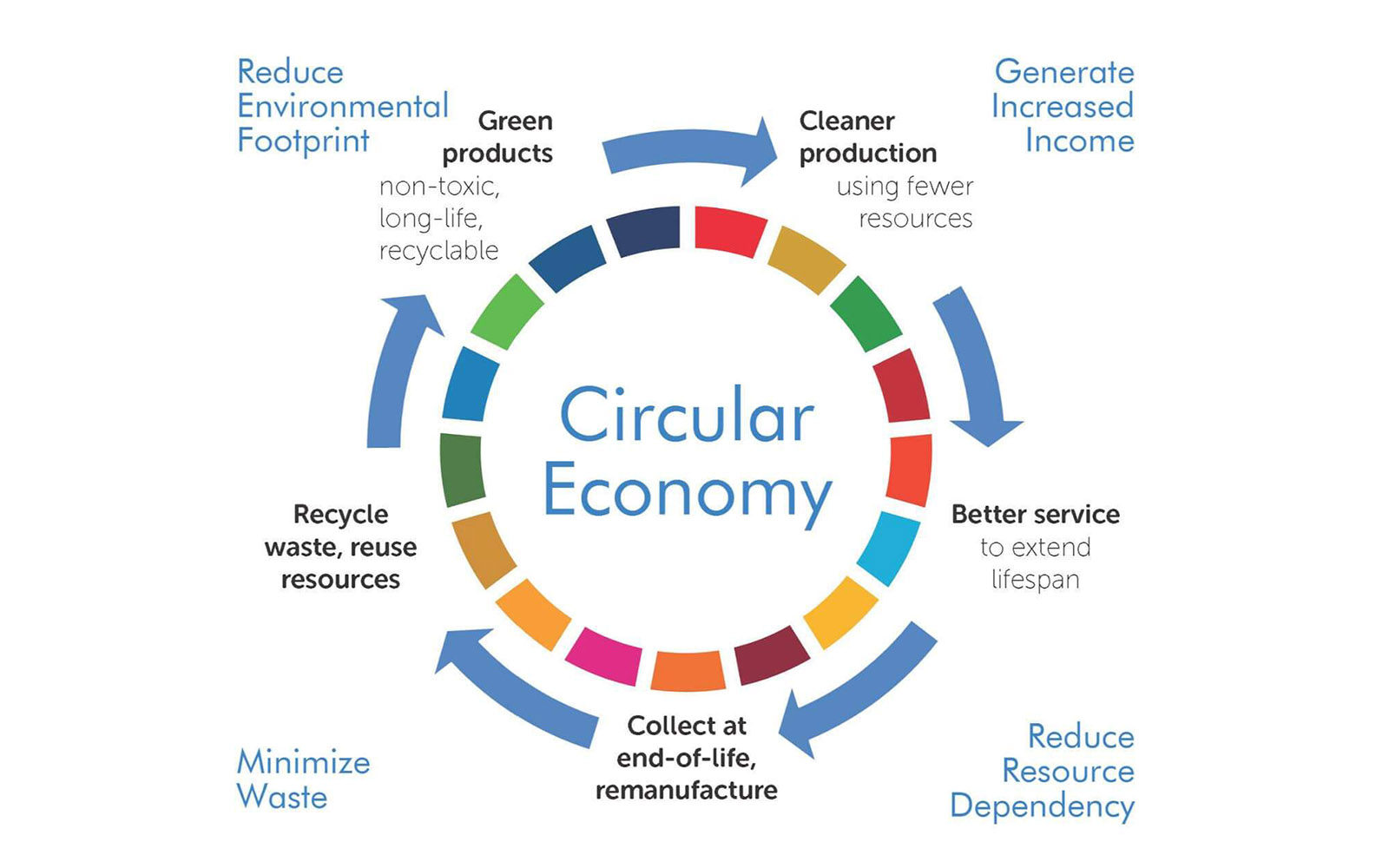
Circular
Economy
A circular economy is the opposite of the linear economy model, which encourages consumers to use and throw away products while damaging natural resources and generating waste. The circular economy is a more resilient and sustainable model which promotes the responsible use and reuse of resources, protection of the environment, reduced greenhouse gas emissions and innovation in waste management. (5)
Photo source: UNIDO
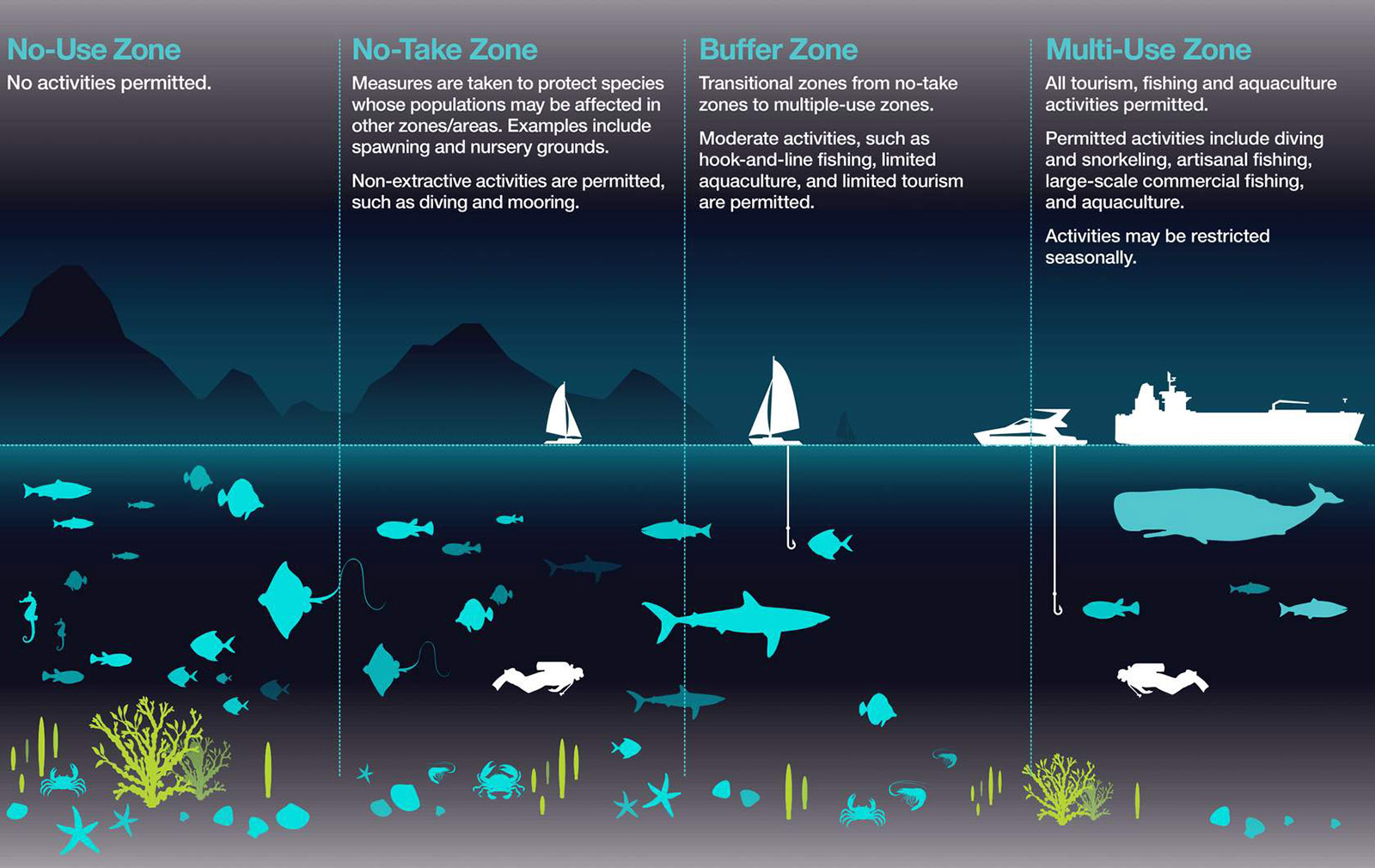
No-Take-Zone
This is an area set aside by the government where no extractive activity is allowed, such as a Marine Protected Area (MPA). Extractive activity is any action that removes, or extracts, any resource; this includes fishing, hunting, logging, mining, and drilling. (National Geographic)
Source: Ocean Health Index
Climate Laws
These are legal frameworks that address climate change-related policy areas, including climate change mitigation and adaptation, disaster risk reduction, or pollution management.
You can find the Climate Change Laws of your country here.
An example of a significant climate legal framework is the Green Deal, a set of policy initiatives taken by the European Commission to help the EU countries become climate-neutral by 2050. It includes a commitment from the EU countries to cut down greenhouse gas emissions, invest in green technologies, and protect the natural environment. (6)
Climate Justice
This is a term which acknowledges that climate change can have differing social, economic, public health and other adverse impacts on historically marginalized or vulnerable communities. (Yale Climate Connections) As not all climate impacts are felt equally by all individuals (because of inequalities that are based on socio-demographic characteristics such as differences in gender, ethnicity, age, or income), climate justice strives to have these inequalities addressed through long-term mitigation and adaptation strategies. Climate justice begins by recognizing the key groups and people that are affected differently by climate change and protecting those who are less resilient.
Transition
In the context of environmental sustainability, transition refers to the changes societies need to make in their core systems in order to achieve their long-term sustainability goals. Some of these systems include food production, energy use, transportation, and construction. (1)
Energy
Efficiency
This means using less energy to perform the same task – that is, eliminating energy waste. Energy efficiency brings a variety of benefits: it reduces greenhouse gas emissions, it decreases the demand for energy imports, and it lowers costs on a household and economy-wide level. (Environmental and Energy Study Institute)

Carbon Sink
This is an area or ecosystem which absorbs more carbon dioxide from the Earth’s atmosphere than it releases. (2) The main natural carbon sinks include soil, oceans and forests. These carbon sinks trap and store atmospheric carbon dioxide in a process called carbon sequestration. However, the carbon stored in natural sinks such as forests can be released back into the atmosphere through forest fires, changes in land use or logging. (3)
Artificial carbon sequestration processes have been developed to extract and store Carbon from the atmosphere or delay/prevent it from being released into the atmosphere. However, artificial carbon sequestration has not acquired the efficiency needed to cope with the extreme effects of climate change. (4) It is crucial to reduce carbon emissions in the first place, in order to aim for climate neutrality. (3)
You can read more about carbon sinks here.
Photo source: Board of Water and Soil Agency
Climate
Neutrality
This refers to reaching and maintaining a balance between emitting greenhouse gases into - and absorbing greenhouse gases from - the atmosphere. It is the same concept as carbon neutrality but it extends to zero net anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions (including emissions beyond carbon dioxide).
Carbon Emissions
Reduction
Reducing carbon emissions refers to the lowering of CO2 gases released into the atmosphere due to human activity. Reducing our carbon emissions helps to ease the pressure on our natural resources and helps slow down climate change. There are various ways of reducing carbon emissions which can have effective impacts on the natural environment. Switching to alternative sources of energy is one of the primary ways to reduce carbon emissions.
Renewable sources of energy such as solar, wind and biomass cannot be depleted and are able to supply a continuous source of clean energy. Even though they still generate some carbon dioxide emissions, these are much lower than the emissions produced by non-renewable resources such as oil or natural gas. Adapting to more sustainable lifestyles and cutting down consumption to preserve nature, forests and biodiversity are still the most impactful ways to prevent irreversible damage.

Carbon
Offsetting
This refers to a reduction in GHG emissions – or an increase in Carbon storage (e.g., through land restoration or the planting of trees) – to compensate for emissions that occur elsewhere. Carbon offsetting is possible because climate change is not just a local problem. Greenhouse gases mix throughout the atmosphere, so reducing them anywhere contributes to overall climate protection. (Carbon Offset Guide) Currently, there are many carbon offsetting projects to which individuals and businesses can contribute which help counteract the emission of GHGs. However, individuals need to carefully select carbon offsetting projects which use certified methods to reduce GHG emissions.
Photo source: UNEP
Carbon
Neutrality
This refers to reaching and maintaining a balance between emitting carbon dioxide into - and absorbing carbon dioxide from - the atmosphere. (3) Carbon neutrality means annual zero net anthropogenic (human-caused or influenced) CO2 emissions. By definition, carbon neutrality means every tonne of anthropogenic CO2 emitted into the atmosphere is compensated with an equivalent amount of CO2 removed. (WRI)
Environmental
Justice
This means the fair treatment and meaningful involvement of all people regardless of race, color, national origin, or income with respect to the development, implementation and enforcement of environmental laws, regulations and policies. Fair treatment means no group of people should bear a disproportionate share of the negative environmental consequences resulting from industrial, governmental and commercial operations or policies. (EPA)

Circular
Economy
A circular economy is the opposite of the linear economy model, which encourages consumers to use and throw away products while damaging natural resources and generating waste. The circular economy is a more resilient and sustainable model which promotes the responsible use and reuse of resources, protection of the environment, reduced greenhouse gas emissions and innovation in waste management. (5)
Photo source: UNIDO

No-Take-Zone
This is an area set aside by the government where no extractive activity is allowed, such as a Marine Protected Area (MPA). Extractive activity is any action that removes, or extracts, any resource; this includes fishing, hunting, logging, mining, and drilling. (National Geographic)
Source: Ocean Health Index
Climate Laws
These are legal frameworks that address climate change-related policy areas, including climate change mitigation and adaptation, disaster risk reduction, or pollution management.
You can find the Climate Change Laws of your country here.
An example of a significant climate legal framework is the Green Deal, a set of policy initiatives taken by the European Commission to help the EU countries become climate-neutral by 2050. It includes a commitment from the EU countries to cut down greenhouse gas emissions, invest in green technologies, and protect the natural environment. (6)
Climate Justice
This is a term which acknowledges that climate change can have differing social, economic, public health and other adverse impacts on historically marginalized or vulnerable communities. (Yale Climate Connections) As not all climate impacts are felt equally by all individuals (because of inequalities that are based on socio-demographic characteristics such as differences in gender, ethnicity, age, or income), climate justice strives to have these inequalities addressed through long-term mitigation and adaptation strategies. Climate justice begins by recognizing the key groups and people that are affected differently by climate change and protecting those who are less resilient.
Do you have questions?
Ask The Earth Prize Mentors!

Advocacy
In addition to personal changes to our individual lifestyles, we can also make a difference and promote change towards sustainability by raising awareness among those around us, and by actively exercising our rights as members of our communities. When we voice our opinion with our family, with our friends, and with our neighbors, we can often influence what actions others take. Getting involved in your local government or community, or in an organization, can also provide an important platform to educate and inspire others, and to drive political decisions on the environment.
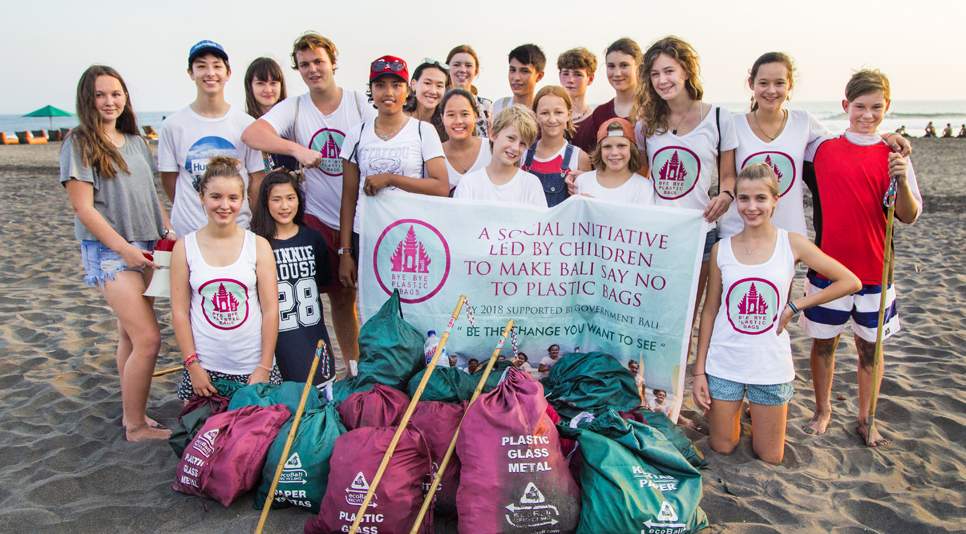
A successful example of advocacy is the Bye Bye Plastic Bags campaign started in 2013 by Balinese sisters, Melati (15) and Isabel (13) Wijsen to spread awareness about plastic pollution and promote the rejection of plastic bags in the island of Bali in Indonesia. Their six-year-long activism and constant petitions played an important role in leading the Balinese government to ban all single-use plastics in 2019. You can read more about Bye Bye Plastic Bags on their website.
Photo source: Bye Bye Plastic Bags

Individual Level
People have an incredible amount of individual power to influence the path our societies follow. As consumers, we are able to shape the economy through our choices: what we choose to buy, what we choose to eat, what we choose to wear… tell manufacturers what they should be making and doing. Through these choices, we can put pressure on businesses to adopt more sustainable practices. As critical thinkers and active individuals, we can also choose to change our habits, join actions that impact our environment positively, and make less environmentally harmful decisions. Together, we can greatly contribute to the global transition towards a more sustainable world.
Responsible Consumption
SDG 12 focuses on responsible consumption and production. Although it covers global-scale action, it can be applied to the individual level. We can become more responsible consumers by:
Buying less! This is simply the most effective solution to overconsumption. Repair what you can and avoid impulse or unnecessary purchases. Become a more informed consumer (know what materials your clothes are made of, where your food comes from…) so when you do need to buy, you can choose the most sustainable option available.
Photo source: UN

Environmental Citizenship
Reducing our waste. This means utilizing lasting, reusable goods (grocery bags, water bottles…), not throwing away food, buying locally sourced and non-packaged produce, composting, and overall, being mindful of how we utilize resources (water, electricity, etc.).
Becoming an environmentally conscious citizen. This is being aware of, and reducing, our use of resources, and understanding the environmental impact of our daily choices and lifestyles.
Here are other tips from the UN Act Now initiative to promote actions that are good for your health and the environment.
Photos source: UN

Advocacy
In addition to personal changes to our individual lifestyles, we can also make a difference and promote change towards sustainability by raising awareness among those around us, and by actively exercising our rights as members of our communities. When we voice our opinion with our family, with our friends, and with our neighbors, we can often influence what actions others take. Getting involved in your local government or community, or in an organization, can also provide an important platform to educate and inspire others, and to drive political decisions on the environment.
A successful example of advocacy is the Bye Bye Plastic Bags campaign started in 2013 by Balinese sisters, Melati (15) and Isabel (13) Wijsen to spread awareness about plastic pollution and promote the rejection of plastic bags in the island of Bali in Indonesia. Their six-year-long activism and constant petitions played an important role in leading the Balinese government to ban all single-use plastics in 2019. You can read more about Bye Bye Plastic Bags on their website.
Photo source: Bye Bye Plastic Bags

Individual Level
People have an incredible amount of individual power to influence the path our societies follow. As consumers, we are able to shape the economy through our choices: what we choose to buy, what we choose to eat, what we choose to wear… tell manufacturers what they should be making and doing. Through these choices, we can put pressure on businesses to adopt more sustainable practices. As critical thinkers and active individuals, we can also choose to change our habits, join actions that impact our environment positively, and make less environmentally harmful decisions. Together, we can greatly contribute to the global transition towards a more sustainable world.
Responsible Consumption
SDG 12 focuses on responsible consumption and production. Although it covers global-scale action, it can be applied to the individual level. We can become more responsible consumers by:
Buying less! This is simply the most effective solution to overconsumption. Repair what you can and avoid impulse or unnecessary purchases. Become a more informed consumer (know what materials your clothes are made of, where your food comes from…) so when you do need to buy, you can choose the most sustainable option available.
Photo source: UN

Environmental Citizenship
Reducing our waste. This means utilizing lasting, reusable goods (grocery bags, water bottles…), not throwing away food, buying locally sourced and non-packaged produce, composting, and overall, being mindful of how we utilize resources (water, electricity, etc.).
Becoming an environmentally conscious citizen. This is being aware of, and reducing, our use of resources, and understanding the environmental impact of our daily choices and lifestyles.
Here are other tips from the UN Act Now initiative to promote actions that are good for your health and the environment.
Photos source: UN

Advocacy
In addition to personal changes to our individual lifestyles, we can also make a difference and promote change towards sustainability by raising awareness among those around us, and by actively exercising our rights as members of our communities. When we voice our opinion with our family, with our friends, and with our neighbors, we can often influence what actions others take. Getting involved in your local government or community, or in an organization, can also provide an important platform to educate and inspire others, and to drive political decisions on the environment.
A successful example of advocacy is the Bye Bye Plastic Bags campaign started in 2013 by Balinese sisters, Melati (15) and Isabel (13) Wijsen to spread awareness about plastic pollution and promote the rejection of plastic bags in the island of Bali in Indonesia. Their six-year-long activism and constant petitions played an important role in leading the Balinese government to ban all single-use plastics in 2019. You can read more about Bye Bye Plastic Bags on their website.
Photo source: Bye Bye Plastic Bags


Example: The Navdanya Biodiversity Farm in Uttarakhand, India
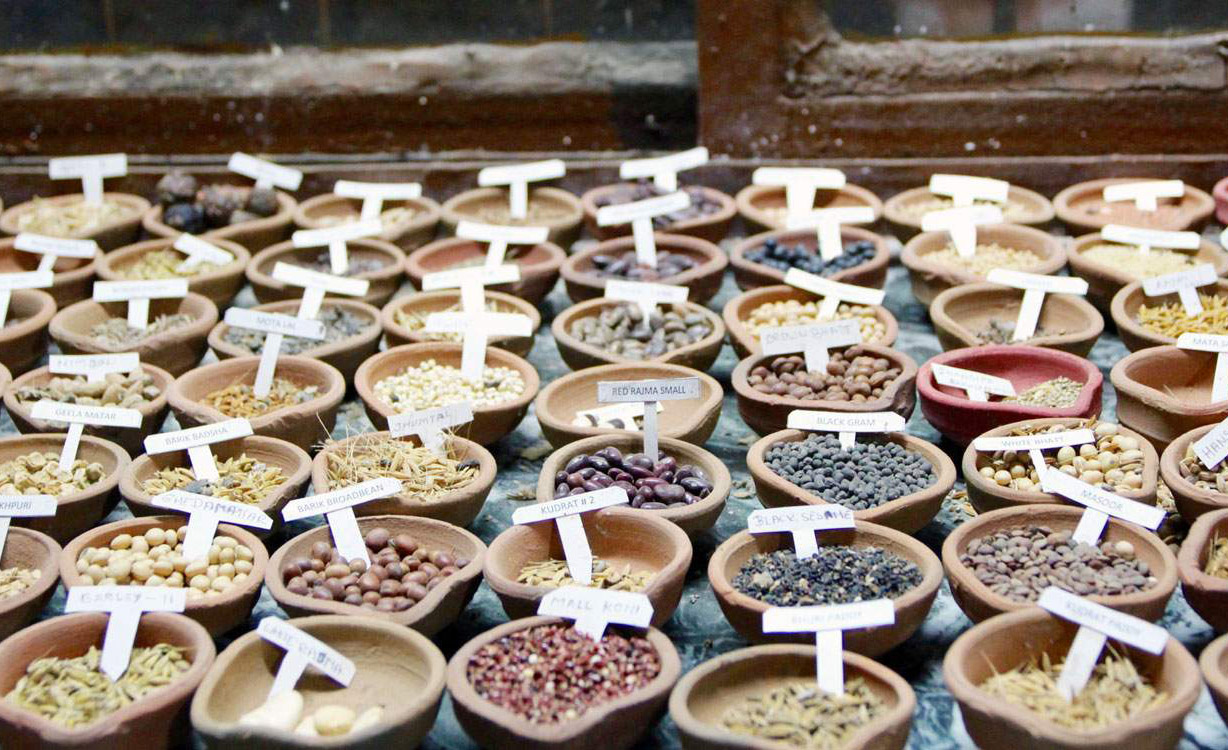
This is an initiative that links seed sharers across India. It has established 122 community seed banks in India and encouraged 5,000,000 farmers to convert to organic farming. Their mission is to improve the well-being of small and marginalized rural farmers through non-violent biodiverse organic farming and fair trade (a trade arrangement that aims to ensure that a set of standards are met in the production and supply of goods, including better prices and working conditions for the producers). (10) While avoiding environmental harm, biodiverse organic farming produces more nutritious food, and brings higher incomes to farmers.
Navdanya’s seed bank has preserved 500 strains of rice and documented 700, preserved 150 strains of wheat and documented 200, as well as protected a multitude of other grains. Their conservation farm has protected a variety of cereals, spices, and medicinal plants in order to preserve their genetic diversity against disease. Watch this video to learn more about Navdanya Biodiversity Farm: The Living Seed
Photo source: FoodPrint

Local Level
The transition towards environmental sustainability can also be driven by action at the local community level. In fact, neighborhoods, towns, and cities around the world are already working towards the adoption of more sustainable policies and practices.
Policy Changes
Local governments have the ability to pass laws that prescribe more sustainable conduct for businesses, organizations, individuals and authorities themselves. One of the main challenges at the local level is how to make cities more sustainable. With more than half of the entire population living in them, cities consume between 60 and 80 percent of the world’s energy and account for 70% of global CO2 emissions. (8) Cities are important for global economic growth but are also responsible for great environmental degradation. (GEF) Following SDG 11, which focuses on building sustainable cities and communities, many cities have started passing laws that are in line with this goal.
You can read more about SDG 11 here.
Example: The Congestion Zone in London
In 2003, a Congestion Charge System was introduced in London with the aim to reduce inner-city traffic and prevent pollution. The system requires a high daily fee for people driving within an 8-square mile radius of central London. (9) The objective of the programme was to reduce the number of private vehicles entering central London during the day and to encourage the use of alternative transportation methods, reducing environmental impacts and in turn, raising substantial revenue. (Centre for Public Impact) This innovative policy has been able to bring about positive changes:
There are 65,000 fewer car trips into or through the charging zone each day, which has helped reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
London’s air quality has been significantly improved, which has positively impacted human health.
Traffic has been reduced by 21%
Between 2016 and 2019, the scale of reduction in nitrogen dioxide (air pollutants) has been five times greater in central London than the national average.
Photo source: AdobeStock

Local Business Practices
Sustainability is perfectly compatible with profitability. In order to ensure a global transition into a more sustainable world, it is crucial that small business owners understand how their companies not only contribute to environmental degradation but also how they can be part of the change.
Agriculture is a sector where local business owners can have a big positive impact on the environment by adopting more sustainable practices. Agriculture is one of the main drivers of environmental degradation and has an enormous environmental footprint. It is directly tied to issues such as soil erosion and deforestation, freshwater overuse, increased GHG emissions and global warming.
A sustainable approach to agriculture refers to farming practices that maximize productivity and profit while minimizing environmental damage. The concept of sustainable agriculture encompasses a wide range of techniques such as organic, free-range, and low-input, which mimic natural ecological processes. Sustainable agriculture farmers can manage water wisely, build and maintain healthy soils, and avoid using pesticides among other practices in order to sustainably use natural resources. Apart from growing food, the core of sustainable agriculture is based on the principle of social justice: the just treatment of farmers and fair food pricing in order to enhance the quality of life of farm families and communities. (National Geographic)
Example: The Navdanya Biodiversity Farm in Uttarakhand, India
This is an initiative that links seed sharers across India. It has established 122 community seed banks in India and encouraged 5,000,000 farmers to convert to organic farming. Their mission is to improve the well-being of small and marginalized rural farmers through non-violent biodiverse organic farming and fair trade (a trade arrangement that aims to ensure that a set of standards are met in the production and supply of goods, including better prices and working conditions for the producers). (10) While avoiding environmental harm, biodiverse organic farming produces more nutritious food, and brings higher incomes to farmers.
Navdanya’s seed bank has preserved 500 strains of rice and documented 700, preserved 150 strains of wheat and documented 200, as well as protected a multitude of other grains. Their conservation farm has protected a variety of cereals, spices, and medicinal plants in order to preserve their genetic diversity against disease. Watch this video to learn more about Navdanya Biodiversity Farm: The Living Seed
Photo source: FoodPrint

Local Level
The transition towards environmental sustainability can also be driven by action at the local community level. In fact, neighborhoods, towns, and cities around the world are already working towards the adoption of more sustainable policies and practices.
Policy Changes
Local governments have the ability to pass laws that prescribe more sustainable conduct for businesses, organizations, individuals and authorities themselves. One of the main challenges at the local level is how to make cities more sustainable. With more than half of the entire population living in them, cities consume between 60 and 80 percent of the world’s energy and account for 70% of global CO2 emissions. (8) Cities are important for global economic growth but are also responsible for great environmental degradation. (GEF) Following SDG 11, which focuses on building sustainable cities and communities, many cities have started passing laws that are in line with this goal.
You can read more about SDG 11 here.
Example: The Congestion Zone in London
In 2003, a Congestion Charge System was introduced in London with the aim to reduce inner-city traffic and prevent pollution. The system requires a high daily fee for people driving within an 8-square mile radius of central London. (9) The objective of the programme was to reduce the number of private vehicles entering central London during the day and to encourage the use of alternative transportation methods, reducing environmental impacts and in turn, raising substantial revenue. (Centre for Public Impact) This innovative policy has been able to bring about positive changes:
There are 65,000 fewer car trips into or through the charging zone each day, which has helped reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
London’s air quality has been significantly improved, which has positively impacted human health.
Traffic has been reduced by 21%
Between 2016 and 2019, the scale of reduction in nitrogen dioxide (air pollutants) has been five times greater in central London than the national average.
Photo source: AdobeStock

Local Business Practices
Sustainability is perfectly compatible with profitability. In order to ensure a global transition into a more sustainable world, it is crucial that small business owners understand how their companies not only contribute to environmental degradation but also how they can be part of the change.
Agriculture is a sector where local business owners can have a big positive impact on the environment by adopting more sustainable practices. Agriculture is one of the main drivers of environmental degradation and has an enormous environmental footprint. It is directly tied to issues such as soil erosion and deforestation, freshwater overuse, increased GHG emissions and global warming.
A sustainable approach to agriculture refers to farming practices that maximize productivity and profit while minimizing environmental damage. The concept of sustainable agriculture encompasses a wide range of techniques such as organic, free-range, and low-input, which mimic natural ecological processes. Sustainable agriculture farmers can manage water wisely, build and maintain healthy soils, and avoid using pesticides among other practices in order to sustainably use natural resources. Apart from growing food, the core of sustainable agriculture is based on the principle of social justice: the just treatment of farmers and fair food pricing in order to enhance the quality of life of farm families and communities. (National Geographic)
Example: The Navdanya Biodiversity Farm in Uttarakhand, India
This is an initiative that links seed sharers across India. It has established 122 community seed banks in India and encouraged 5,000,000 farmers to convert to organic farming. Their mission is to improve the well-being of small and marginalized rural farmers through non-violent biodiverse organic farming and fair trade (a trade arrangement that aims to ensure that a set of standards are met in the production and supply of goods, including better prices and working conditions for the producers). (10) While avoiding environmental harm, biodiverse organic farming produces more nutritious food, and brings higher incomes to farmers.
Navdanya’s seed bank has preserved 500 strains of rice and documented 700, preserved 150 strains of wheat and documented 200, as well as protected a multitude of other grains. Their conservation farm has protected a variety of cereals, spices, and medicinal plants in order to preserve their genetic diversity against disease. Watch this video to learn more about Navdanya Biodiversity Farm: The Living Seed
Photo source: FoodPrint


Greenwashing
“Greenwashing is the process of conveying a false impression or providing misleading information about how a company's products are more environmentally sound. Greenwashing is considered an unsubstantiated claim to deceive consumers into believing that a company's products are environmentally friendly.” (Investopedia) Companies use a variety of techniques to signal sustainability such as including the colour green in their logo and using words such as “responsible”, “conscious”, or “natural” on their packaging. Some companies secretly fund newspaper articles to make them appear virtuous when they are not.
It is always important to consider these claims from an informed standpoint - by researching the ingredients within a product, reading about the certifications they bear, and understanding the scale of the companies’ sustainability efforts in comparison to their potential and competitors. As some certification labels sound more sustainable than they truly are, it is also important to understand their certification criteria.
Global Level
Global challenges require global efforts and commitments. Even if as individuals and communities we can significantly contribute to societies’ transition towards environmental sustainability, the most decisive changes need to come from global political institutions, national governments, and large corporations.
National Governments
Governments have the power to take positive environmental action within their territories through national legislation. Countries can approve laws, regulations, decrees, and procedures to bring about change towards environmental sustainability. It is important to mention that this type of legislation is usually defined by how environmentally conscious are the citizens and their legal representatives. There are many examples of national legislation driving positive change around the world:
In 2008, Ecuador became the first country in the world to recognize the rights of nature in its constitution, giving citizens the authority to petition on behalf of ecosystems, and requiring the government to remedy violations of nature’s rights. (11)
Rwanda established a ban on non-biodegradable plastic bags in 2008, which prohibited the manufacturing, importation, use and sale of plastic bags across the country. In 2019, this ban was extended to include all single-use plastics - the first ban of its kind in the African continent. (12) Although Rwanda still struggles with plastic smugglers (13), the ban has had a great positive impact on the country’s tourism and economy. (14)
Multilateral Agreements
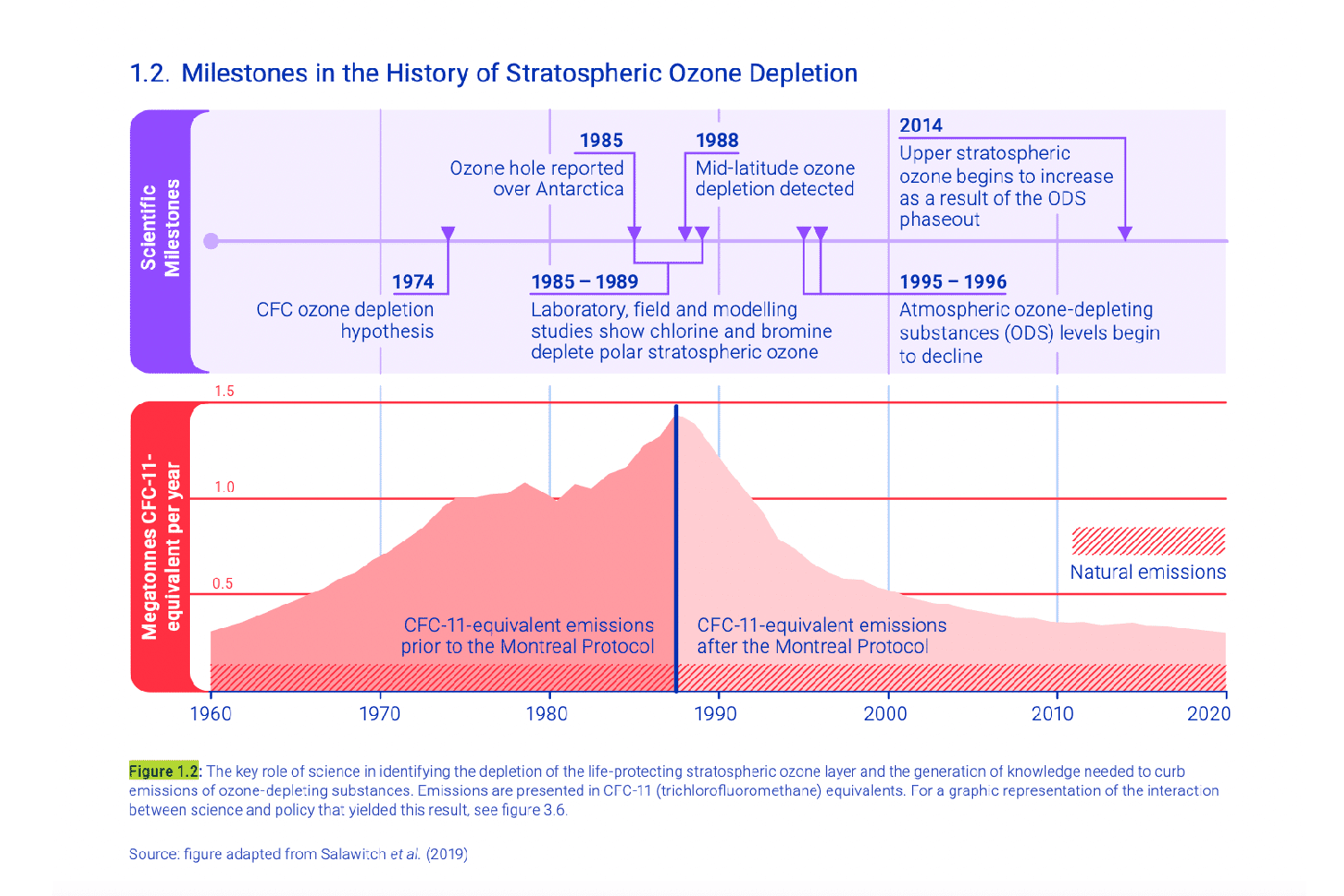
Multilateral environmental agreements (MEAs) are legally-binding treaties, conventions and protocols signed between three or more nations to express a shared commitment to achieve a specific environmental goal. Currently, there are over 250 MEAs in force that target different environmental issues. (15) One of the earliest landmark agreements is the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, signed in 1987 by all 198 UN Member States. This agreement regulated the use of chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which destroy our planet’s ozone layer - a protective shield (including humans) against the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation. This MEA is particularly significant because it successfully led to the elimination of 99% of ozone-depleting substances and it remains to this day the only UN treaty to have ever been ratified by every country in the world. (CFR)
Source: firuge adapted from Salawitch el al. (2019)
Multinational Corporations
A major problem with large multinational corporations is that the premise under which they frequently operate - maximizing profits and minimizing costs - leaves environmental costs associated with their activities out of the equation. A large percentage of them have their production factories set up in developing countries, where social and environmental regulations are more relaxed. (16) However, multinational companies play a large part in environmental degradation. Alone, these giants account for nearly one-fifth of global CO2 emissions. Many of these companies’ emissions are higher than the emissions of some countries.
Recently, however, it has become evident that multinational corporations are indispensable allies in the global transition towards environmental sustainability. Sustainability has also become an important concern for their consumers and shareholders. Thus, most companies seem to have shifted to more sustainable practices and products. Given these trends, and consumers’ readiness to pay more for sustainable products (17), companies have a high incentive to present their products as sustainable. However, sometimes the claims on a product’s packaging or advertisement may be misleading or false - and many companies have been found to be involved in greenwashing.
Photo source: Sean Pollock/Unsplash

Greenwashing
“Greenwashing is the process of conveying a false impression or providing misleading information about how a company's products are more environmentally sound. Greenwashing is considered an unsubstantiated claim to deceive consumers into believing that a company's products are environmentally friendly.” (Investopedia) Companies use a variety of techniques to signal sustainability such as including the colour green in their logo and using words such as “responsible”, “conscious”, or “natural” on their packaging. Some companies secretly fund newspaper articles to make them appear virtuous when they are not.
It is always important to consider these claims from an informed standpoint - by researching the ingredients within a product, reading about the certifications they bear, and understanding the scale of the companies’ sustainability efforts in comparison to their potential and competitors. As some certification labels sound more sustainable than they truly are, it is also important to understand their certification criteria.
Global Level
Global challenges require global efforts and commitments. Even if as individuals and communities we can significantly contribute to societies’ transition towards environmental sustainability, the most decisive changes need to come from global political institutions, national governments, and large corporations.
National Governments
Governments have the power to take positive environmental action within their territories through national legislation. Countries can approve laws, regulations, decrees, and procedures to bring about change towards environmental sustainability. It is important to mention that this type of legislation is usually defined by how environmentally conscious are the citizens and their legal representatives. There are many examples of national legislation driving positive change around the world:
In 2008, Ecuador became the first country in the world to recognize the rights of nature in its constitution, giving citizens the authority to petition on behalf of ecosystems, and requiring the government to remedy violations of nature’s rights. (11)
Rwanda established a ban on non-biodegradable plastic bags in 2008, which prohibited the manufacturing, importation, use and sale of plastic bags across the country. In 2019, this ban was extended to include all single-use plastics - the first ban of its kind in the African continent. (12) Although Rwanda still struggles with plastic smugglers (13), the ban has had a great positive impact on the country’s tourism and economy. (14)
Multilateral Agreements
Multilateral environmental agreements (MEAs) are legally-binding treaties, conventions and protocols signed between three or more nations to express a shared commitment to achieve a specific environmental goal. Currently, there are over 250 MEAs in force that target different environmental issues. (15) One of the earliest landmark agreements is the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, signed in 1987 by all 198 UN Member States. This agreement regulated the use of chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which destroy our planet’s ozone layer - a protective shield (including humans) against the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation. This MEA is particularly significant because it successfully led to the elimination of 99% of ozone-depleting substances and it remains to this day the only UN treaty to have ever been ratified by every country in the world. (CFR)
Source: firuge adapted from Salawitch el al. (2019)

Multinational Corporations
A major problem with large multinational corporations is that the premise under which they frequently operate - maximizing profits and minimizing costs - leaves environmental costs associated with their activities out of the equation. A large percentage of them have their production factories set up in developing countries, where social and environmental regulations are more relaxed. (16) However, multinational companies play a large part in environmental degradation. Alone, these giants account for nearly one-fifth of global CO2 emissions. Many of these companies’ emissions are higher than the emissions of some countries.
Recently, however, it has become evident that multinational corporations are indispensable allies in the global transition towards environmental sustainability. Sustainability has also become an important concern for their consumers and shareholders. Thus, most companies seem to have shifted to more sustainable practices and products. Given these trends, and consumers’ readiness to pay more for sustainable products (17), companies have a high incentive to present their products as sustainable. However, sometimes the claims on a product’s packaging or advertisement may be misleading or false - and many companies have been found to be involved in greenwashing.
Photo source: Sean Pollock/Unsplash

Greenwashing
“Greenwashing is the process of conveying a false impression or providing misleading information about how a company's products are more environmentally sound. Greenwashing is considered an unsubstantiated claim to deceive consumers into believing that a company's products are environmentally friendly.” (Investopedia) Companies use a variety of techniques to signal sustainability such as including the colour green in their logo and using words such as “responsible”, “conscious”, or “natural” on their packaging. Some companies secretly fund newspaper articles to make them appear virtuous when they are not.
It is always important to consider these claims from an informed standpoint - by researching the ingredients within a product, reading about the certifications they bear, and understanding the scale of the companies’ sustainability efforts in comparison to their potential and competitors. As some certification labels sound more sustainable than they truly are, it is also important to understand their certification criteria.
Do you have questions?
Ask The Earth Prize Mentors!
THIS WEBSITE USES COOKIES
We use cookies to provide you with the best possible experience. They also allow us to analyze user behavior in order to constantly improve the website for you. You can read more about our Cookie Policy and Privacy Policy.

